Thalassemia is a genetically inherited blood disorder which is characterized by the production of less or abnormal hemoglobin. As we know, hemoglobin is a protein found in Red Blood Cells. Hemoglobin is responsible for carrying oxygen around in the body. Thalassemia results in large numbers of red blood cells being destroyed, which leads to anemia. As a result of anemia, person affected with Thalassemia will have pale skin, fatigue and dark coloration of urine.
Genetics of Thalassemia
Hemoglobin is made up of two smaller protein molecules called alpha globin and beta globin. In humans, four genes are responsible for coding alpha globin protein and two genes code for beta globin protein.
If any of the four genes responsible for making alpha globin is missing or mutated — abnormal alpha globin will be produced. This causes alpha-thalassemia disorder.
Similarly, if any of the two genes responsible for making beta globin is missing or mutated — abnormal beta globin will be produced. This causes beta-thalassemia disorder.
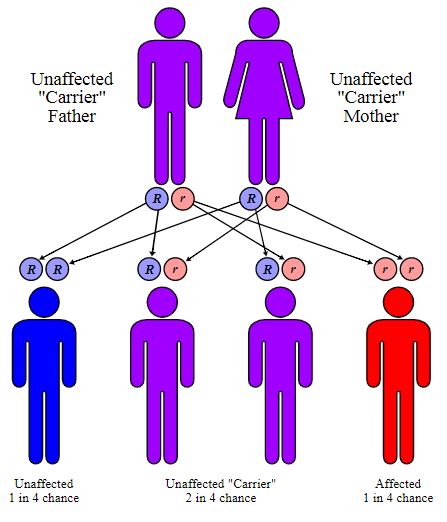
Thalassemia is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern of genetic inheritance. If both parents are carrier of Thalassemia, there are 25% chance that the child will be normal, 25% chance that the child will develop thalassemia and 50% chance that the child will also become a carrier (meaning the child will develop no/minor symptoms of thalassemia but he can transfer the disorder to next generation)
Thalassemia Major
Thalassemia major occurs when the child inherits two copies of mutated genes; one from each parent. In thalassemia major, the affected person develops symptoms of thalassemia. Such persons lacks the ability to produce normal, adult hemoglobin and experience chronic fatigue due to anemia.
Treatment of Thalassemia Major
The only treatment to combat severe anemia is regular blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy.
Thalassemia as a Disability
In India, thalassemia is considered a disability under RPWD Act 2016. This act enables people with thalassemia to avail disability benefits.
Thalassemia Minor
If a person receives one mutated copy of the gene from one parent and one normal copy of the gene from second parent, then the person will be a thalassemia minor patient. Such people are carrier of disorder and they may develop only minor symptoms of thalassemia.
Thalassemia Meaning in Hindi
In Hindi, thalassemia is written as थैलेसीमिया
Following video explains all about thalassemia in Hindi language.
Thalassemia Diagnosis
Presence of mutated gene that causes thalassemia can be easily detected with a special blood test called hemoglobin electrophoresis. This test can reveal whether a person is thalassemia carrier or not.

Life Expectancy of a Person with Thalassemia
A person with the thalassemia trait has a normal life expectancy. However, heart complications arising from beta thalassemia major can make this condition fatal before the age of 30 years.
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
"Thalassemia: Disability, Types, Major, Minor." Wecapable.com. Web. July 27, 2024. <https://wecapable.com/thalassemia-disability-types-major-minor/>
Wecapable.com, "Thalassemia: Disability, Types, Major, Minor." Accessed July 27, 2024. https://wecapable.com/thalassemia-disability-types-major-minor/
"Thalassemia: Disability, Types, Major, Minor." (n.d.). Wecapable.com. Retrieved July 27, 2024 from https://wecapable.com/thalassemia-disability-types-major-minor/

Is minor thalassemia is eligible for disable certificate
Is BETA THALASSEMIA MINOR eligible for disability certificate?
yes, reservation to thalassemia affected people should be given to avoid discrimination.