Spina Bifida is one of the most common neurological birth defects affecting approximately 3 out of 10,000 children born worldwide. It is a neural tube defect that causes improper development of the spine and spinal cord in a fetus. Though there was a time when it was seen as a childhood disability today many adults are living successfully with Spina Bifida.
In this write-up, we will be sharing information about causes of Spina Bifida, its treatment, and life management, etc. Read on to understand this birth defect more clearly.
Spina Bifida: Overview
Spina Bifida is a neurological birth defect affecting the growth of the spine and spinal cord in an embryo. The complication manifests itself during the first few weeks of pregnancy. It affects the neural tube of the growing fetus. A neural tube is a structure in a fetus that eventually develops into the baby’s brain, spinal cord, and the tissues surrounding them.
Normally, a neural tube is formed early in pregnancy and it closes around the 28th day after the conception. When this neural tube does not develop or does not close properly it causes defects of the spinal cord and the bones of the spine. The defect can occur anywhere along the spine if the neural tube does not close properly along the way. Non-closing of the neural tube often causes damage to the spinal cord and nerves. Depending on the location, size, defect, and complications; Spina Bifida may range from mild to severe. Normally, the higher the location of the defect on the spine the more severe are the complications and disability.
Causes and Risk Factors
Like the majority of birth defects, the exact cause for Spina Bifida is unknown to the medical fraternity. However, there are certain risk factors that increase the risk of Spina Bifida. Some of the common risk factors of Spina Bifida include –
- Folate Deficiency – Folate, the natural form of Vitamin B9, is important for the proper development of an embryo. Therefore, deficiency of folate increases the risk of neural tube defects, including Spina Bifida.
- Genetics – Though the majority of children born with Spina Bifida are born to parents with no history of the condition in the family, doctors see genetics as one of the risk factors. Women with Spina Bifida or other neural defects have a higher chance of giving birth to a child with Spina Bifida. Moreover, if parents give birth to a child with Spina Bifida, the risk of a second child being born with the same condition increases.
- Some medications – A few medicines, when taken during pregnancy, are considered as risk factors for Spina Bifida. For example, medicines for seizures, like valproic acid, are considered risky as they interfere with the body’s ability to use folate or folic acid.
- Uncontrolled diabetes – Women with uncontrolled blood sugar levels are at higher risk of birthing a child with Spina Bifida.
- Pre-pregnancy obesity – While weight gain is normal in pregnancy, pre-pregnancy obesity may increase the risk of birth defects like Spina Bifida.
- Hyperthermia – An increased body temperature during early pregnancy increases the risk of Spina Bifida. This increase in temperature may be due to natural reasons like fever or may be due to activities like a hot bath or sauna.
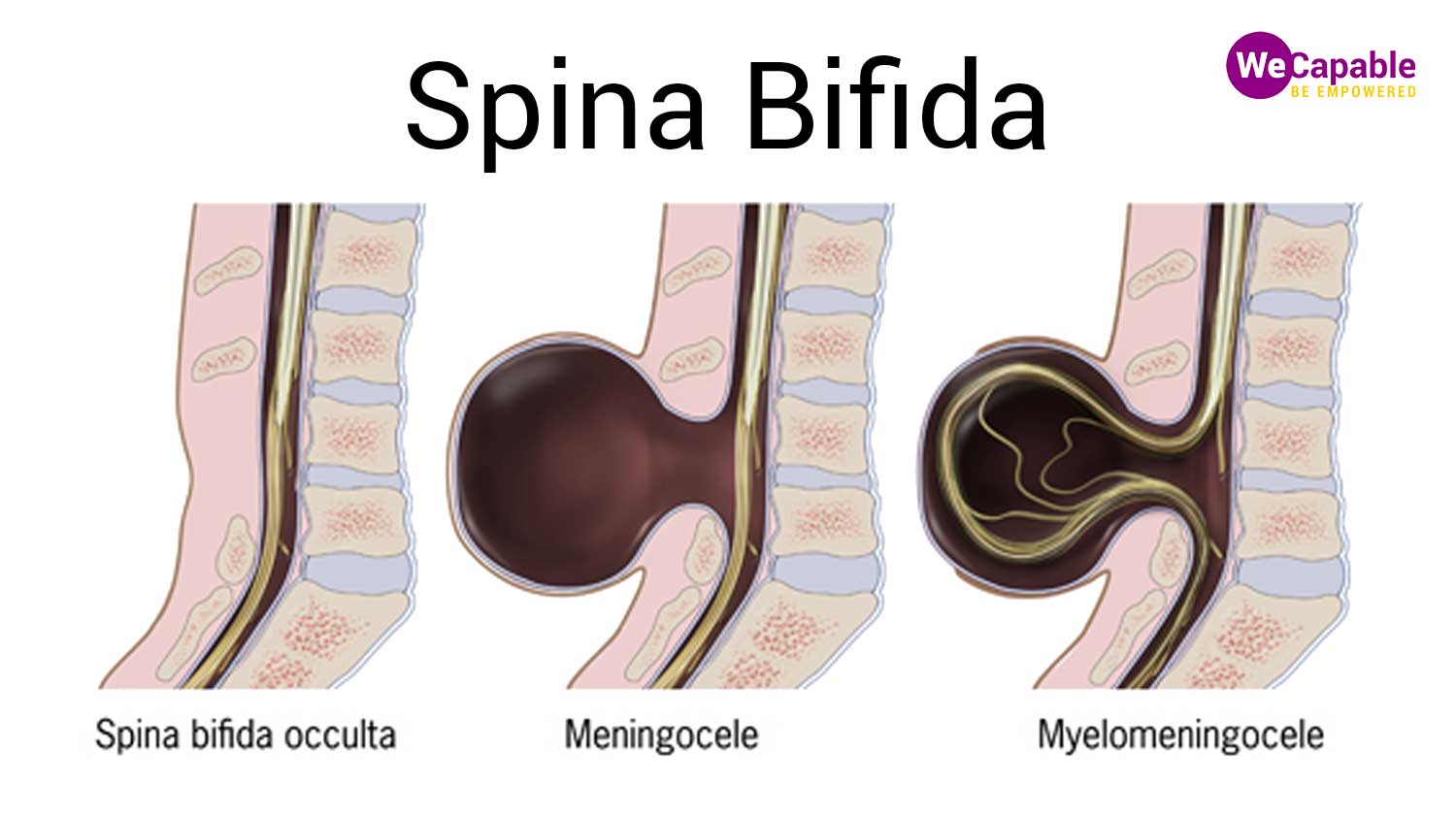
Types of Spina Bifida
Spina Bifida may occur in different forms and varying severity. Two main types of Spina Bifida are –
- Spina Bifida Occulta – It is the most common and mildest form of Spina Bifida. It causes a small gap or separation between one or more vertebrae. Typically, there are no signs or symptoms, and many a time the survivor doesn’t know that she has a birth defect unless it is found in imaging done due to unrelated reasons. However, in some individuals, Spina Bifida Occulta may show some signs like an abnormal tuft of hair, dimple, or a birthmark at the affected area.
- Myelomeningocele – It is the most severe type of Spina Bifida that causes many complications for the survivor. In this type of Spina Bifida, the spinal canal is open along several vertebrae in the lower or middle back. The membrane and spinal nerves push through the openings at birth forming a sac on the baby’s back. The tissues and nerves are usually exposed though sometimes it is covered with skin. Babies with Myelomeningocele are prone to life-threatening infections. It may also cause paralysis and bladder and bowel dysfunction.
Medical Care
Infants born with Spina Bifida Occulta normally do not have symptoms or complications due to their condition hence they only require pediatric care like other infants.
On the other hand, children born with Myelomeningocele typically have many complications that can affect their normal living. These babies are diagnosed with Spina Bifida before birth or right after birth. Depending on the symptoms and severity of symptoms the survivor may need medical attention throughout their lives.
Complications caused due to Spina Bifida
Severe cases of Spina Bifida may have caused many complications including severe physical disabilities. The severity of the complications depend mainly on three factors –
- Size and location of the defect
- Whether the protruding sac is covered by skin or not
- The spinal nerve coming out of the affected area
We are providing an exhaustive list of complications caused due to Spina Bifida. However, you should know that all these symptoms are seldom present in any one child with Spina Bifida. The severity of each complication too varies from child to child.
1. Mobility Issues
The nerves controlling the leg muscles below the area affected by Spina Bifida do not function properly thus causing mobility issues. In severe cases, it may cause complete paralysis of the legs. Whether a child with Spina Bifida can walk or not depends on different factors including – location of the defect, the size, and the care received before and after the birth.
2. Orthopedic Complications
Children with severe cases of Spina Bifida may grow with several other orthopedic complications because of the weak muscles in the legs and back. The exact complication depends on the location of the defect. The probable orthopedic complications include –
- Scoliosis (abnormal sideways curve of the spine)
- Abnormal growth of the lower body
- Dislocation of the hip bones and joints
- Deformities of the bones and joints
- Muscle contractures
3. Bowel and Bladder Complications
The nerves controlling the bowel and bladder come from the lowest level of the spinal cord. So, in most cases of severe Spina Bifida bladder and bowels don’t function properly.
4. Hydrocephalus
Babies born with myelomeningocele typically are affected with hydrocephalus i.e. accumulation of fluid in the brain. This requires immediate medical attention. The accumulated fluid needs to be drained through a shunt or it can cause serious issues like brain hemorrhage. However, the shunt inserted in the brain may also sometimes get infected and cause several complications seizure, fixed downward gaze, etc.
5. Chiari Malformation Type II
It is one of the common brain abnormalities that occur in children with myelomeningocele Spina Bifida. The brainstem in this case gets elongated and is positioned lower than normal. This abnormality can cause breathing and swallowing issues.
6. Meningitis
In some cases, severe Spina Bifida may cause meningitis i.e. infection in the tissues surrounding the brain. This infection may sometimes prove life-threatening for the baby and cause brain injury or other such issues.
7. Sleep Apnea
Children and adults with Spina Bifida may experience sleep disorders like sleep apnea. The person may experience difficulty in breathing while sleeping.
8. Sexual Dysfunction
While fertility in most people with Spina Bifida is intact studies reveal that many males with Spina Bifida may experience sexual dysfunctions including erectile dysfunction and retrograde ejaculation.
9. Higher Risks of other complications
Individuals with Spina Bifida are at an increased risk of many health complications like latex allergy, urinary tract infection, gastrointestinal disorders and depression, etc. Children with myelomeningocele may also develop learning disabilities.
Prevention
Being a structural defect, there’s no cure for Spina Bifida. However, parents may act cautiously to prevent their unborn babies from getting this neural tube birth defect. As mentioned earlier, the most prominent reason for Spina Bifida is a deficiency of folate. So, taking folic acid supplements from one month before conception to the end of the first trimester can hugely reduce the risk of Spina Bifida and other neural tube defects.
Because many women don’t discover their pregnancy in early stage, some experts recommend a daily dose of 400 to 1000 mcg folic acid supplement for all women of childbearing age. Including foods containing natural folate in daily diet is also a good idea but folate is not so easily absorbed by the body as folic acid. So, for some women folic acid supplement is the better choice. Women with Spina Bifida, diabetes, and seizure requires a higher dose of folic acid supplement for the purpose.
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
"Spina Bifida: A Disability Caused due to Malformed Spinal Cord." Wecapable.com. Web. June 18, 2025. <https://wecapable.com/spina-bifida-disability/>
Wecapable.com, "Spina Bifida: A Disability Caused due to Malformed Spinal Cord." Accessed June 18, 2025. https://wecapable.com/spina-bifida-disability/
"Spina Bifida: A Disability Caused due to Malformed Spinal Cord." (n.d.). Wecapable.com. Retrieved June 18, 2025 from https://wecapable.com/spina-bifida-disability/

Leave a Reply