Specific Learning Disabilities is a group of disabling conditions that hampers a person’s ability to listen, think, speak, write, spell, or do mathematical calculations. One or more of these abilities may be hampered.
Specific Learning Disability interferes with the normal learning process of the person. The term does not include learning problems that are primarily the result of visual, hearing or motor disabilities, of mental retardation, of emotional disturbance, or of environmental, cultural or economic disadvantage.
Types and Examples of Specific Learning Disabilities
1. Dyslexia
Dyslexia is the specific learning disability in reading. Children affected with dyslexia find it very difficult to read. It occurs in children with normal vision and intelligence.
Symptoms of Dyslexia in School going Kids
- Reading well below the expected level for age
- Problems remembering the sequences
- Difficulty in seeing similarities and differences in letters and words
- Difficulty in spelling words
- Avoiding activities that involve reading
2. Dysgraphia
Dysgraphia is a specific learning disability that affects written expression, for example difficulties with spelling, poor handwriting and trouble putting thoughts on paper.
Symptoms of Dysgraphia in School going Kids
- Difficulty in writing letters
- Trouble in spacing letters correctly on the page
- Difficulty in writing in a straight line
- Difficulty in:
- Holding paper with one hand while writing with the other
- Holding and controlling a pencil or other writing tool
- Putting the right amount of pressure on the paper with a writing tool
- Maintaining the right arm position and posture for writing

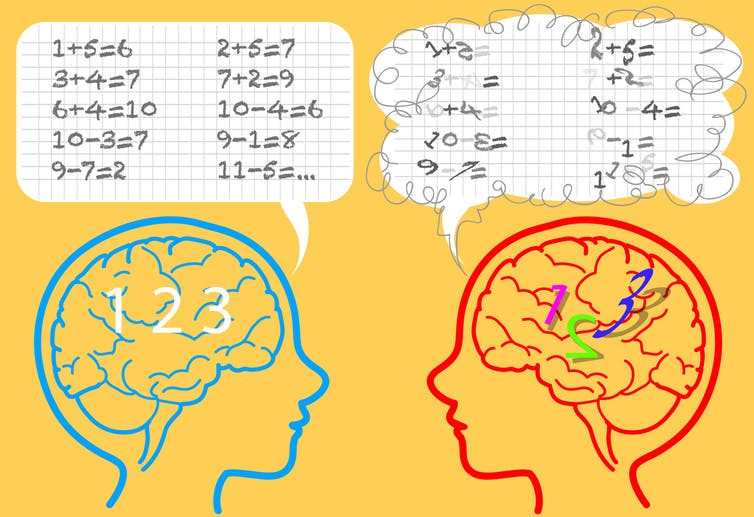
3. Dyscalculia
Dyscalculia is a specific learn disability that causes difficulty in learning arithmetic, understanding numbers and doing mathematical calculations. About 3 to 6% of population is affected with some degree of dyscalculia.
- Difficulty reading analog clocks
- Difficulty in finding which of two numbers is larger
- Issues in sequencing things
- Difficulty with multiplication, subtraction, addition, and division tables, mental arithmetic, etc.
- Problems with differentiating between left and right
- Difficulty with time, directions, recalling schedules, sequences of events, keeping track of time, frequently late or early
- Inability to concentrate on mentally intensive tasks

NOTE: The term acalculia is used for an acquired impairment in which people have difficulty in performing simple. Acalculia is distinguished from dyscalculia in that acalculia is acquired late in life due to neurological injury such as stroke, while dyscalculia is a specific developmental disorder first observed during the acquisition of mathematical knowledge.
4. Dyspraxia
Developmental co-ordination disorder (DCD), also known as dyspraxia, is a condition affecting physical co-ordination. It causes a child to perform less well than expected in daily activities for their age, and appear to move clumsily.
5. Developmental Aphasia
Aphasia is an impairment of language, affecting the production or comprehension of speech and the ability to read or write. Aphasia is always due to injury to the brain-most commonly from a stroke, particularly in older individuals.
Specific Learning Disabilities and Disability Benefits
India’s RPWD Act 2016 defines Specific Learning Disabilities as a heterogeneous group of conditions wherein there is a deficit inprocessing language, spoken or written, that may manifest itself as a difficulty to comprehend, speak, read, write, spell, or to do mathematical calculations and includes such conditions as perceptual disabilities, dyslexia, dysgraphia, dyscalculia, dyspraxia and developmental aphasia.
Disability Certificate
The teachers of the public and private school shall carry out the screening in Class III or at eight years of age, whichever is earlier. The screening test is given in Figure 2. If in the screening shows test three or more answers are in “frequently” column, then the child should be referred for further assessment.
Every school (public and private) shall have a screening committee headed by the principal of the school. After applying the screening test, if an anomaly is detected then, the teacher should bring it to the notice of principal and screening committee of the school. The teachers shall interview the parents to assess their involvement and motivation regarding their child’s education. If the parents are motivated and screening questionnaire suggests SLD, then child should be referred for further assessment.
The child shall be referred to pediatrician for SLD assessment by the principal of the school with the recommendations of the screening committee endorsed.
Medical Authority
The Medical Superintendent or Chief Medical Officer or Civil Surgeon or any other equivalent authority as notified by the State Government shall be head the certification authority. The medical authority will comprise of:
- The Medical Superintendent or Chief Medical Officer or Civil Surgeon or any other equivalent authority as notified by the State Government
- Pediatrician or Pediatric Neurologist (where available)
- Clinical or Rehabilitation Psychologist
- Occupational therapist or Special Educator or Teacher trained for assessment of SLD.
Validity of Disability Certificate
The certification will be done for children aged eight years and above only. The child will have to undergo repeat certification at the age of 14 years and at the age of 18 years. The certificate issued at 18 years will be valid life-long.
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
"Specific Learning Disability: Definition, Examples, Types." Wecapable.com. Web. April 28, 2024. <https://wecapable.com/specific-learning-disability-definition-examples-types/>
Wecapable.com, "Specific Learning Disability: Definition, Examples, Types." Accessed April 28, 2024. https://wecapable.com/specific-learning-disability-definition-examples-types/
"Specific Learning Disability: Definition, Examples, Types." (n.d.). Wecapable.com. Retrieved April 28, 2024 from https://wecapable.com/specific-learning-disability-definition-examples-types/

Sir, my son is a slow writer. He can’t complete his writing task in allotted time. Due to this he scored very less percentage in his 10th board exams. Now he is 11th . He doesn’t have any other problem like learning , understanding and in mathematics. Even writing is also neat and clear. Does this problem comes under learning disability? Can we have any facility like scribe in 12th board exams?
sorry no, you should work on his speed by giving 20 pages in a hour and see how many he can complete also you can say him ..forget about his hand writing just complete in an hour and just keep one thing in mind handwriting should be understandable only ….I am sure this formula will help you a lot
Sir does Downs Syndrome come under learning disability?
Hello, sir. I am 22 years old and I was recently diagnosed with dyscalculia and dyspraxia. Can I get a disability certificate for the same from IBHAS?
I think you should be able to get the disability certificate from IBHAS. However, if they are not authorized, they will tell you which hospital to contact.
My son has the problem of dyscalculia as well as learning Disabilities. I have got the certificate from a private hospital, named child first clinic in New Delhi. Can this certificate work or I need the government certificate also and could you help me out where I can get if it is so. We are residing in Mehrauli, New Delhi.