Hearing impairment is a partial or total inability to hear. It is a disability which is sub-divided in two categories of deaf and hard of hearing.
- “Deaf” means persons having 70 dB hearing loss in speech frequencies in both ears.
- “Hard of hearing” means person having 60 dB to 70 dB hearing loss in speech frequencies in both ears.
A pure tone audiometry test measures the softest, or least audible, sound that a person can hear. During the test, you will wear earphones and hear a range of sounds directed to one ear at a time. The loudness of sound is measured in decibels (dB).
Assessment of Hearing Impairment
Measurement of Air Conduction Thresholds (ACT)
- ACT is to be measured using standard Pure Tone Audiometry by an Audiologist for Right Ear and Left Ear separately
- In case of non-reliable ACT, additional tests are recommended such as Immittance, and Speech audiometry or Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) Testing
- Measuring ACT may be difficult in children aged 3-5 years. In such cases, Conditioned Pure Tone audiometry/Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (VRA) shall be conducted. ABR or Auditory Steady State Response (ASSR) testing can be advised for the estimation of ACT in infant and young children
Computation of Percentage of Hearing Disability
- Calculate Pure tone average of ACT for 500 Hz, 1000 Hz, 2000 Hz, 4000 Hz for Right Ear and Left ear separately (whenever there is no response at any frequency ACT is to be considered as 95dB)
- Monaural percentage of hearing disability is to be calculated as per the ready reckoner given below separately for Right Ear and Left Ear
| Monaural PTA in dB | % of Disability |
|---|---|
| 0 to 250 | 0 |
| 26 | 1 |
| 27 | 1 |
| 28 | 1 |
| 29 | 1 |
| 30 | 1 |
| 31 | 1 |
| 32 | 1 |
| 33 | 1 |
| 34 | 2 |
| 35 | 3 |
| 36 | 4 |
| 37 | 5 |
| 38 | 6 |
| 39 | 7 |
| 40 | 8 |
| 41 | 9 |
| 42 | 10 |
| 43 | 11 |
| 44 | 12 |
| 45 | 13 |
| 46 | 14 |
| 47 | 15 |
| 48 | 16 |
| 49 | 17 |
| 50 | 18 |
| 51 | 19 |
| 52 | 20 |
| 53 | 21 |
| 54 | 22 |
| 55 | 23 |
| 56 | 24 |
| 57 | 25 |
| 58 | 26 |
| 59 | 27 |
| 60 | 40 |
| 61 | 41.71 |
| 62 | 43.42 |
| 63 | 45.13 |
| 64 | 46.84 |
| 65 | 48.55 |
| 66 | 50.26 |
| 67 | 51.97 |
| 68 | 53.68 |
| 69 | 55.39 |
| 70 | 57.1 |
| 71 | 58.81 |
| 72 | 60.52 |
| 73 | 62.23 |
| 74 | 63.94 |
| 75 | 65.65 |
| 76 | 67.36 |
| 77 | 69.07 |
| 78 | 70.78 |
| 79 | 72.49 |
| 80 | 74.2 |
| 81 | 75.91 |
| 82 | 77.62 |
| 83 | 79.33 |
| 84 | 81.04 |
| 85 | 82.75 |
| 86 | 84.46 |
| 87 | 86.17 |
| 88 | 87.88 |
| 89 | 89.59 |
| 90 | 91.3 |
| 91 | 93.01 |
| 92 | 94.72 |
| 93 | 96.43 |
| 94 | 98.14 |
| 95 | 100 |
Formula for Calculating Percentage of Hearing Disability
Percentage of Hearing Disability = (Better ear % of hearing disability x 5) + (Poorer ear % of hearing disability) / 6
WHO Hearing Impairment Grading
| Grade of impairment* | Corresponding audiometric ISO value** | Performance | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| * Grades 2, 3 and 4 are classified as disabling hearing impairment (for children, it starts at 31 dB) ** The audiometric ISO values are averages of values at 500, 1000, 2000, 4000 Hz. | |||
| 0 – No impairment | 25 dB or better (better ear) | No or very slight hearing problems. Able to hear whispers. | |
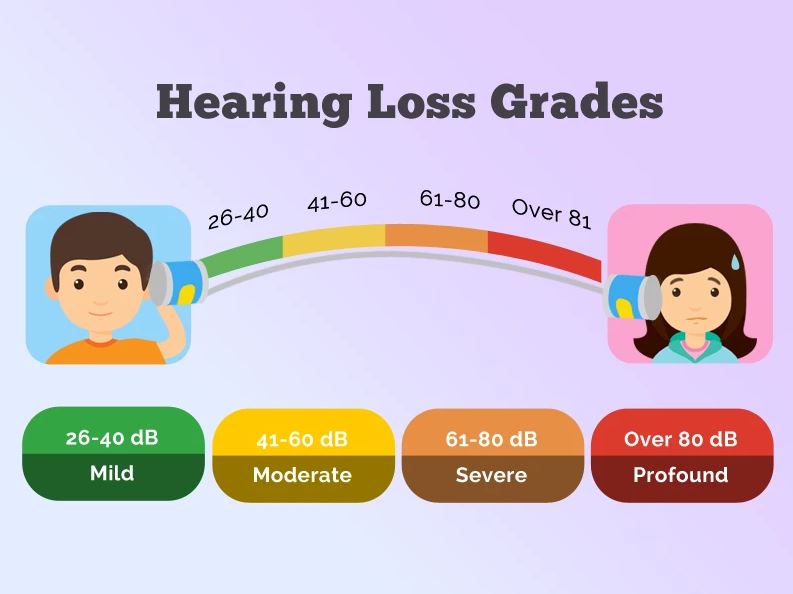
| 1 – Slight impairment | 26-40 dB (better ear) | Able to hear and repeat words spoken in normal voice at 1 meter. | Counseling. Hearing aids may be needed. |
| 2 – Moderate impairment | 41-60 dB (better ear) | Able to hear and repeat words spoken in raised voice at 1 meter. | Hearing aids usually recommended. |
| 3 – Severe impairment | 61-80 dB (better ear) | Able to hear some words when shouted into better ear. | Hearing aids needed. If no hearing aids available, lip-reading and signing should be taught. |
| 4 – Profound impairment including deafness | 81 dB or above (better ear) | Unable to hear and understand even a shouted voice. | Hearing aids may help understanding words. Additional rehabilitation needed. Lip-reading and sometimes signing essential. |
Disability Benefits
Hearing Impairment is recognized as a disability under RPWD Act 2016 in India. People with benchmark hearing disability can claim benefits provided under various government schemes. You should visit a government hospital to get disability certificate for hearing impairment.
Use the citation below to add this article to your bibliography
"Hearing Impairment Disability Definition and Types." Wecapable.com. Web. July 27, 2024. <https://wecapable.com/hearing-impairment-disability-definition-and-types/>
Wecapable.com, "Hearing Impairment Disability Definition and Types." Accessed July 27, 2024. https://wecapable.com/hearing-impairment-disability-definition-and-types/
"Hearing Impairment Disability Definition and Types." (n.d.). Wecapable.com. Retrieved July 27, 2024 from https://wecapable.com/hearing-impairment-disability-definition-and-types/

Respect Lalit sir,
I am Abhishek Mahto from Jharkhand.
Sir, Maine ek udid card ka form bhara tha, to mujhe udid card mila lekin expiry ho gaya hai.
lekin mujhe renew karana hai, jo maine udid ke website mein jakar bharne ki koshish ki. phir accept nahin kar raha hai….plz help me…how to do??
There is a separate link for renewal. http://www.swavlambancard.gov.in/pwd/pwdrenewalcard
Although since you had asked nearly six months ago, I hope you have already got the link and applied for renewal. Best of Luck.
Hello, I have complete loss of hearing in my left ear since birth but I can hear with the right ear. I am 21 years old. Can government allow me a disability certificate?
Hello sir , I have complete loss of hearing(dead) in my left ear since birth but I can hear with the right ear. I am 18 years old. Can government allow me a disability certificate?
Unfortunately, no. Please refer to the formula given above to assess disability percentage. {(Better Ear % x 5) + (Poor Ear %)}/6
If your better ear is free of any impairment and poor ear is 100% impaired, then your effective impairment comes to, 100/6 = 16.67%.
I have a friend with same condition as yours. Hence, I speak from experience.
I have 60 db loss of hearing in left ear and 20 db loss in right ear. Can govt will allow me disability certificate??
Hii aapko reply Mila
Same problem I have been faced but I have this problem in my right ear from birth time
I don’t know how to get PWD certificate for it
Disability Benefits:
Hearing Impairment is recognized as a disability under RPWD Act 2016 in India. People with benchmark hearing disability can claim benefits provided under various government schemes. You should visit a government hospital to get disability certificate for hearing impairment.
Hello I am a speech therapist for ECI I recently enrolled a deaf child who’s family is also deaf. Due to Covid all of our therapies are through telehealth I was wondering if there’s a way to interpret verbal language into ASL through telehealth ?
What is the maximum and minimum decibel limit within which disability certificate can be issued
I have had moderate hearing loss since 6 yr of age due to measles. Am now 72 years old. Did not wear hearing aids until age 30 so learned to lip read and ask lots of questions, sat in the front of classrooms aetc.
My question, I have very selective tolerance for noise. Wear hearing aids (one vs. two and other more difixations) varying my hearing experience to levels of sound I can tolerate.
Are there others like me? My husband can’t understand why I would want to modify my world of sounds.
I suffer from tinnitus and had many episodes of vertigo which attacks me at any time. I am a government employee serving the public. Is Meniere’s disease not considered a disability ?
Hello sir, Please share hearing loss in decibel terms and its percentage mentioning in the hearing disability certificate.
My right ear got suddenly affected 3 years ago. After getting checked at the GH Hospital through ESIC, they confirmed moderate loss (40 to 60 db) of hearing. They advised me to use hearing aid. Can I apply for disability certificate? Please advise. My Age 55.
Hello sir,
My audiogram test report is right ear 100dBHL and left ear 83 dBHl. And my bera test report is wave morphology fair. Peck V could be traced upto 70dBnHL in right ear and upto 60 dBnHL in left ear hence, expected PTA2 should be 60 dBHL and 50 dBHL respectively. But government hospital issuance disability certificate percentage 22%
Sir, please count my disability certificate percentage
Hello sir, I have hearing loss of 65db in both ears. Can I get disability certificate? Does 65db calculate to 40% disability?